$ touch Temperature_ETL.sh
$ gedit Temperature_ETL.shRemote Sensor API Data
Case Study 1
Import sensor data using API, load transformed data to a reporting API as CSV file. Schedule cronjob to run every minute
- Report temperature statistics for a remote location
- hourly average, min and max temp
- remote temp sensor
- update every minute
- load results in file
Temperature_ETL.sh
- Given:
get_temp_apito read temp from remote sensorload_stats_apito load stats to dashboard repository
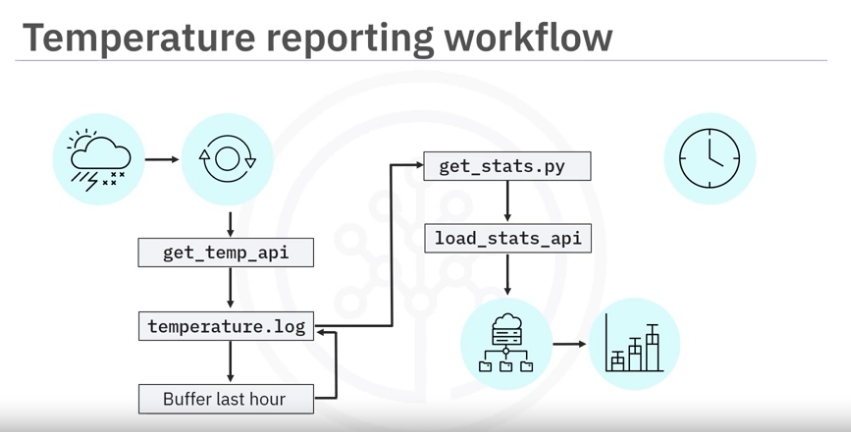
workflow
- The extraction step involves obtaining a current temperature reading from the sensor using the supplied get _temp_api
- Append the reading to a log file, say temperature.log.
- Since you will only need to keep the most recent hour of readings, buffer the last 60 readings and then just overwrite the log file with the buffered readings.
- Call a python script called get_stats.py, which calculates the temperature stats from the 60-minute log and
- Loads the resulting stats into the reporting system using the load_stats_api.
- The stats can then be used to display a live chart showing the hourly min, max, and average temperatures.
- You will also want to schedule your workflow to run every minute.
Solution
Create file
- Start by creating a shell script called Temperature_ETL.sh.
- You can edit the file in gedit or any other text editor you wish to use
- Here is the command to open filename
- You can create the file by using the touch command.
Add comments
- In the editor, type in the bash shebang to turn your file into a bash shell script.
- Add the following comments to help outline your tasks.
- Extract a temperature reading from the sensor using the supplied get_temp_api.
- Append the reading to a log file, say temperature.log.
- You only need to keep the most recent hour of readings, so buffer the last 60 readings.
- Call a program say a Python script called get_stats.py, which calculates the temperature stats from the 60-minute log and
- load the resulting stats into the reporting system using the supplied API.
- After you finish writing the ETL bash script, you will need to schedule it to run every minute.
# Enter this into the file:
#! /bin/bash
# Extract reading with get_temp_api
# Append reading to temperature.log
# Buffer last hour of readings (last 60 readings)
# Call get_stats.py to aggregate the readings
# Load the stats using load_stats_apiExtract Data from Sensors
- Now you can fill in some details for your task comments start by initializing your temperature log file on the command line with the touch command.
- In the text editor, enter a command to call the API to read a temperature and
- append the reading to the temperature log
- Now just keep the last hour or 60 lines of your log file by overwriting the temperature log with its last 60 lines.
$ touch Temperature_ETL.sh
#! /bin/bash
# Extract reading with get_temp_api and append reading to temperature.log
get_temp_api >> temperature.log
# Buffer last hour of readings (last 60 readings)
tail -60 temperature.log > temperature.logTransform Data
- Suppose you have written a Python script called get_stats.py which
- reads temperatures from a log file, calculates the temperature stats,
- and writes the results to an output file so that the input and output file names are specified as command-line arguments.
- You can add the following line to your ETL script, which calls Python3 and invokes your Python script get_stats.py using the readings in temperature.log
- and writes the temperature stats to a CSV file called temp_stats.csv.
- This completes the transformation component of your ETL script.
# Call get_stats.py to aggregate the readings
python3 get_stats.py temperature.log temp_stats.csvLoad Data
- Finally, you can load the resulting stats into the reporting system using the supplied API by calling the API and specifying the temp_stats.csv as a command-line argument.
# Load the stats using load_stats_api
load_stats_api temp_stats.csvSet Permissions
- Next, don’t forget to set permissions for the script file, to make your shell script executable.
$ chmod +x Temperature_ETL.shSchedule ETL
- Now it’s time to schedule your ETL job.
- Open the crontab editor.
- Schedule your job to run every minute of every day,
- close the editor, and save your edits.
$ crontab -e
1 * * * * path/Temperature_ETL.shYour new ETL job is now scheduled and running in production.